CDNs are often employed by website owners, content suppliers, e-commerce platforms, and online services to optimise content delivery, enhance user experience, and lessen the burden on origin servers. Web domains may guarantee quicker load times, lower latency, and improved worldwide accessibility for their visitors by utilising a CDN. In this article we will learn about CDN, what is CDN, How CDN works? and more.
What is a CDN?
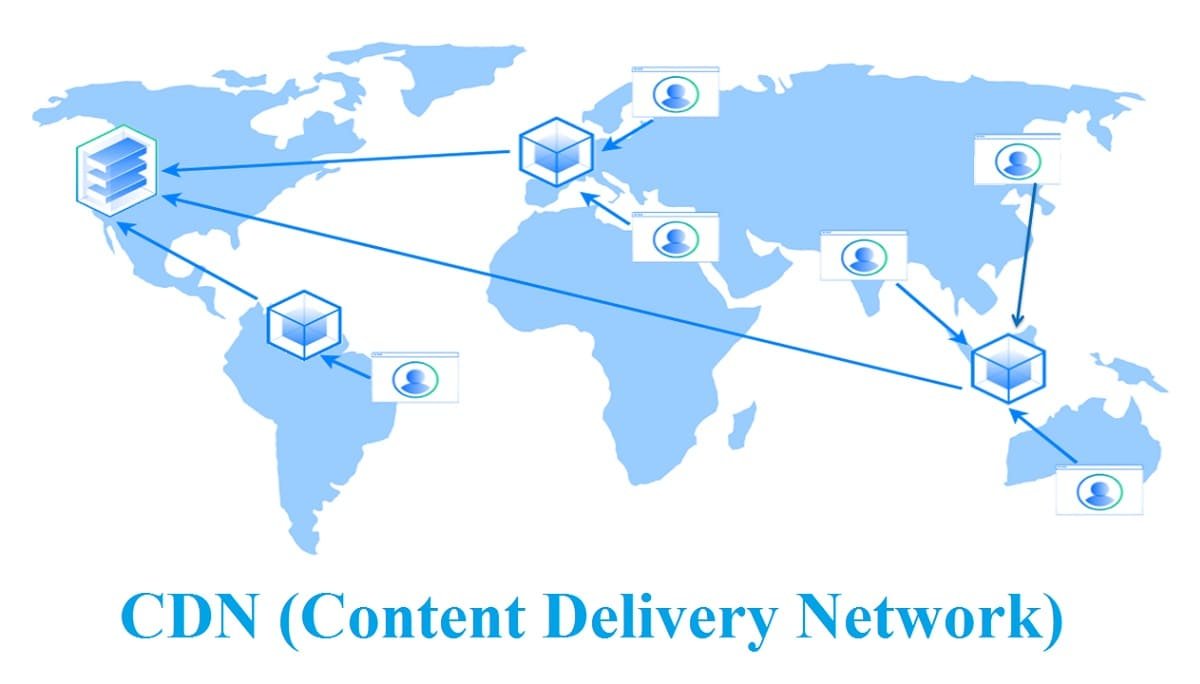
CDN stands for Content Delivery Network. It is a network of geographically dispersed servers that collaborate to effectively provide online content to users according on their location, including photos, videos, stylesheets, scripts, and other resources. By caching and providing content from a server closer to the end user, a CDN primarily serves to minimise latency and enhance website performance.
How does a CDN Work?
The way content delivery networks (CDNs) operate is by distributing website content and resources among a network of edge servers or points of presence (PoPs) that are scattered geographically. A CDN's main objective is to optimise content delivery and boost the functionality of websites and online applications. Here is a step-by-step explanation of how a CDN works -
1. Content Replication - When a website owner decides to use a CDN, they replicate their website's static content (e.g., images, videos, stylesheets, scripts) onto the CDN's edge servers. This procedure, which is frequently automated, makes sure that the identical content is accessible in several locations throughout the world.
2. DNS Resolution - When a user makes an access request to a website that makes use of a CDN, their browser sends a DNS query to convert the website's domain name into an IP address. Based on the user's location, the domain's DNS server returns the IP address of the closest CDN edge server.
3. Edge Server Selection - In order to reply to the user's request, the CDN's load balancer or routing algorithm chooses the best edge server. Common selection criteria include proximity to the server, server availability, network circumstances, and server load.
4. Content Delivery - The requested content is served directly to the user's browser after the suitable edge server has been selected. Without the need to get it from the website's origin server, content that has already been cached on the edge server may be sent rapidly (as is typically the case with frequently requested pages).
5. Caching - Content that is often accessed is cached on edge servers by CDNs. The CDN can offer the cached copy of a resource when a user requests one, avoiding the need to fetch it from the origin server. The caching speeds up content delivery and considerably lessens the burden on the origin server.
6. Dynamic Content Acceleration - Although the main purpose of CDNs is to cache static content, some sophisticated CDNs also include tools to optimise the delivery of dynamic content. This may be done by using dynamic content compression, clever caching strategies, and other approaches to speed up processing and decrease data transfer.
7. Load Balancing - To distribute incoming user requests throughout their network of edge servers, CDNs employ load balancing algorithms. This guarantees that no one server is overwhelmed and enhances the CDN's responsiveness and performance.
8. Real-time Analytics and Monitoring - Website owners may measure different performance indicators, such as bandwidth use, cache hit/miss ratios, response times, and user geographic distribution, using the real-time analytics and monitoring tools that CDNs frequently offer. These insights aid in CDN configuration optimisation and problem identification.
9. Security and DDoS Protection - Many CDNs include security tools like Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) to shield websites from dangers like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) assaults. Before harmful traffic reaches the origin server, the CDN may filter and reduce it.
Website owners may boost worldwide accessibility, decrease latency, handle traffic surges, and guarantee a more seamless user experience for visitors from all over the world by utilising a CDN.
Who uses a CDN?
Many people, companies, organisations, and content providers use CDNs to improve the speed of their websites and online applications and to optimize the distribution of web content. Some of the common users of CDNs include -
1. Website Owners - CDNs are used by individuals, small businesses, and large companies who run websites to enhance user experience, speed up load times, and enhance website performance.
2. E-commerce Platforms - Online shops and e-commerce platforms make use of CDNs to guarantee quick and dependable delivery of product photos, descriptions, and other content to clients, improving the shopping experience.
3. Media and Entertainment Companies - Media firms, multimedia streaming platforms, and video-on-demand services all make use of CDNs to effectively reach their worldwide consumers with high-quality video and audio content.
4. News and Media Websites - To manage abrupt traffic increases during breaking news events, news websites and online publishers employ CDNs, guaranteeing that their articles, photographs, and videos are promptly accessible to visitors.
5. Software and App Developers - Utilising CDNs may speed up the delivery of patches, app installs, and software upgrades, lowering server load and download times.
6. Social Media Platforms - CDNs are used by social media platforms and websites to quickly and effectively provide user-generated movies, photos, and content to millions of people all over the world.
7. Gaming Companies - Online gaming companies use CDNs to improve the gaming experience by speeding up the delivery of patches, downloads, and game updates as well as lowering latency while playing.
8. Educational Institutions - Globally accessible course contents, lecture videos, and educational resources are made possible through the usage of CDNs by universities, schools, and online learning platforms.
9. Content Creators and Bloggers - In order to optimise the loading times of their articles, photographs, and multimedia content, bloggers, vloggers, and content producers gain from CDNs. This helps them draw in and keep their audience.
10. Government and Non-profit Organizations - For users and stakeholders to have timely access to crucial information and resources, government websites, nonprofits, and public services employ CDNs.
11. Cloud Service Providers - Cloud computing companies employ CDNs to hasten the delivery of data, apps, and content to customers from their cloud infrastructure.
12. Mobile App Developers - To enhance the user experience for mobile users, mobile app developers employ CDNs to optimise the distribution of app content, media, and updates.
Implementing a CDN may be advantageous for everyone who manages a website, web application, or online business. CDNs are useful tools for expanding worldwide accessibility, lowering latency, handling traffic spikes, and effectively distributing content to people all over the world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a Content distribution Network (CDN) is a distributed network of geographically separated computers created to improve the effectiveness and performance of content distribution over the internet. The way CDNs operate is by carefully placing many edge servers in various areas and replicating website content, such as photos, videos, stylesheets, and scripts. A user's request for content from a website that makes use of a CDN is routed to the closest edge server, which lowers latency and speeds up loading. In order to provide rapid delivery without retrieving from the origin server, CDNs utilise caching technologies to store frequently visited content on their edge servers.
A wide spectrum of consumers, such as website owners, e-commerce platforms, media firms, software developers, educational institutions, social media platforms, and others, benefit from CDNs. Users may optimise website speed, manage traffic surges, increase worldwide accessibility, and guarantee a more seamless user experience by utilising a CDN.
In today's digital environment, CDNs are an essential tool because of their critical role in streamlining content delivery, decreasing server load, and improving overall performance of websites and online apps.
FAQs
What is a CDN, and how does it work?
A CDN is a network of geographically dispersed servers that uses its closest server location to cache and provide website content to consumers. A CDN reduces latency and speeds up loading times by delivering material from the nearest edge server when a user requests it from a website.
Why should I use a CDN for my website?
Using a CDN may dramatically enhance website performance by decreasing load times, cutting latency, and effectively dispersing traffic. Additionally, it improves user experience, helps manage traffic spikes, and offers more security against specific kinds of intrusions.
Which types of content can be delivered through a CDN?
The material that CDNs may offer includes HTML files, movies, stylesheets, scripts, HTML files, and downloadable files. A CDN essentially allows any static or dynamic material that a website offers to its visitors to be optimised.
Do CDNs handle dynamic content?
Although CDNs are mostly intended for caching and providing static material, some sophisticated CDNs also include methods for optimising the delivery of dynamic content. This might involve carefully storing dynamic material or using other techniques to speed up processing.
How does a CDN improve website speed?
A CDN reduces the physical distance that data must travel by providing content from servers located close to the user, resulting in lower latency and quicker loading times. The requirement to continually request material from the origin server is also removed by caching frequently used content on edge servers.
Is a CDN suitable for small websites or only large-scale applications?
CDNs are beneficial for websites of all sizes. Even tiny websites can see increased performance and dependability, especially if they have visitors from multiple areas. Larger websites with worldwide audiences can considerably benefit from CDNs owing to the vast spread of servers.
How do I set up a CDN for my website?
Joining a CDN provider, setting up your domain's DNS settings to refer to the CDN, and ensuring sure your website assets are appropriately optimised and cached for distribution through the CDN are the steps involved in setting up a CDN for your website.
Which are some popular CDN providers?
Popular CDN companies include, among others, Cloudflare, Akamai, Amazon CloudFront, Microsoft Azure CDN, Fastly, and CDN77. The features and price offered by each supplier may vary, so it's important to pick one that meets your unique requirements.
Does using a CDN affect SEO (Search Engine Optimization)?
In general, using a CDN has a favourable effect on SEO. Improved website performance and quicker load times can lead to better user experience, which search engines take into account when determining rankings. Additionally, CDNs can aid in reducing server response times and enhancing accessibility, both of which are crucial for SEO.
Is a CDN a replacement for website hosting?
No, a CDN is not a replacement for website hosting. By streamlining content distribution and offloading traffic from the origin server, CDNs enhance website hosting. The website's core hosting server is still in charge of producing dynamic content and handling user requests while CDNs manage content distribution.
Do CDNs support HTTPS and SSL/TLS encryption?
Yes, most modern CDNs support HTTPS (HTTP Secure) and SSL/TLS encryption. Data transmission between the end user and the CDN server is encrypted and secured against eavesdropping and tampering thanks to the usage of SSL certificates.
Can a CDN help with website scalability during traffic spikes?
Yes, handling traffic surges and spreading the load over different servers is one of CDNs' primary advantages. The origin server may concentrate on handling more resource-intensive activities by outsourcing content delivery to the edge servers, which increases the website's scalability during times of heavy demand.
How much does a CDN cost?
Utilising a CDN has a range of costs based on the CDN provider, the volume of data transported, the quantity of requests, and any additional services or features needed. While some CDNs have tiered pricing based on consumption levels, others provide free services for minimal usage.
Is there any downtime risk with a CDN?
Although CDNs are designed to be extremely dependable, like other technologies, they occasionally experience outages. To reduce the danger of downtime, respectable CDN providers, however, use redundant systems and have many data centres. Some CDNs also have failover features that allow traffic to be sent to different servers in the event of problems.
Can a CDN help with global website accessibility?
Yes, CDNs greatly increase the accessibility of websites worldwide by delivering content from servers located all over the world. This lessens the effect of physical distance-related latency, ensuring visitors from various areas have quicker load times and a better surfing experience.
Can a CDN improve mobile website performance?
Yes, CDNs may enhance the functionality of mobile websites by lowering page load times and streamlining information delivery to mobile devices. This is essential since different network conditions frequently affect mobile users, and quicker load times can increase user engagement.
Does using a CDN affect website analytics and tracking?
Using a CDN could have some impact on website analytics and tracking. While some CDNs may mask client IP addresses with the CDN's IP address, others may include functionalities that properly relay client IP addresses to the origin server. The influence of the CDN should be taken into consideration while configuring analytics tools, according to website owners.
How can I monitor the performance of my CDN?
The majority of CDN providers include dashboards and performance monitoring tools that let website owners keep tabs on data regarding user geographic distribution, response times, bandwidth use, and cache hit/miss ratios. These metrics aid website owners in identifying possible problems and optimising CDN settings.
What happens if a file is updated on my website? How does the CDN handle updates?
The CDN must be notified when a file on your website is updated so it may update its cache with the most recent copy. Many CDNs include techniques for content invalidation or cache purging, which let website owners launch updates and remove outdated information from edge servers.
Can I use a CDN for my web application APIs or backend services?
Yes, certain CDNs are made to facilitate backend service caching and speed up API delivery. They may be set up to send dynamic API replies more efficiently, lightening the strain on servers and improving API performance.
To know more about our platform, visit our About Us page.
Comments